Looking for a highly customisable way to get instant alerts from your smart home directly on your desktop, especially when other solutions haven't quite met your needs?
Many users, myself included, have found that while solutions like the Home Assistant Companion App offer a great starting point for notifications, they sometimes don't consistently deliver rich media (like Frigate snapshots) or seamlessly unify all voice alerts across different systems. If you've encountered similar challenges, or simply prefer a more hands-on approach to tailor your notifications exactly how you like them, this guide is for you. In my experience, this custom-built solution has provided reliable visual and audio alerts, giving me complete control over my desktop notifications.
With this setup, you can expect:

Of course, if you have other operating systems and you are happy to try yourself, then that's up to you. I only have Windows and Debian and that's why I did this.
All the example setup is done with 4 cameras but can easily be changed depending on your setup.
Ready to take control of your home security alerts and finally get the desktop notifications that truly meet your needs? Let's get started.
Even though I have found this reliable, please note if you decide to follow my guide you are doing it at your own risk and I am not liable for anything that might go wrong.
Before we dive into the desktop magic, let's make sure your core smart home components are in place. These steps are the same regardless of whether you're using Windows or Debian.
You'll need a running **Frigate** instance that's detecting objects and publishing events to an **MQTT broker**.
events and snapshot data to MQTT. If you need help with Frigate's initial setup, check the official Frigate documentation.To configure your config.yaml and Node-RED flow correctly, you'll need to know the exact MQTT topics Frigate is publishing. There are a couple of easy ways to find these:
MQTT Explorer is a fantastic desktop application that allows you to easily inspect all traffic on your MQTT broker. This is often the quickest way to see the topics and payloads in real-time.
192.168.1.100), Port (usually 1883), and the Username/Password you set up for your MQTT user.frigate/.frigate/YOUR_CAMERA_NAME/person (for person detection events)frigate/YOUR_CAMERA_NAME/person/snapshot (for the actual image data)frigate/YOUR_CAMERA_NAME/car (for car detection events)frigate/YOUR_CAMERA_NAME/car/snapshot (for car image data)config.yaml and Node-RED flow.You can also listen to MQTT topics directly from within Home Assistant's Developer Tools.
frigate/# (this is a wildcard that will listen to all topics starting with `frigate/`).config.yamlThis file holds all the key settings for your desktop notifier, like MQTT connection details, camera names, and the exact phrases for your voice alerts.
C:\Users\YOUR_WINDOWS_USERNAME\Documents\FrigateNotifier~/FrigateNotifier (This means /home/YOUR_USERNAME/FrigateNotifier)config.yaml: Inside this new folder, create a new text file and name it config.yaml.config.yaml file.
# config.yaml
# Configuration for the Windows/Linux Frigate Notifier Script
mqtt:
broker: "YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_IP" # IMPORTANT: Replace with your MQTT broker's IP address or hostname (e.g., 192.168.1.100)
port: 1883
username: "YOUR_MQTT_USERNAME" # IMPORTANT: Replace with your actual MQTT username
password: "YOUR_MQTT_PASSWORD" # IMPORTANT: Replace with your actual MQTT password
control_topic: "notifier/control"
snapshot_base_topic: "notifier/" # Base topic for camera snapshots (e.g., notifier/camera_one/snapshot) No need to change this line!
general_settings:
image_cache_dir: "MotionNotifierCache" # For Windows: relative path; For Linux: will be ~/.cache/MotionNotifierCache
cooldown_period_seconds: 10 # Minimum time between image pop-ups from ANY camera (per camera)
enable_large_image_popup: true
large_image_display_duration_seconds: 5
image_display_width: 320 # Width for the image pop-up
image_display_height: 240 # Height for the image pop-up
fixed_offset_x: 10 # Offset from right of screen
fixed_offset_y: 10 # Offset from bottom of screen
border_width: 3
window_internal_padding: 5
text_label_height_estimate: 25
tts_script_path: "tts_speaker.py" # Relative to notifier script's directory. ENSURE THE CORRECT tts_speaker.py FOR YOUR OS IS IN THIS DIRECTORY.
tts_enabled_on_startup: true # Initial state of global TTS toggle
initial_volume: 1.0 # Initial TTS volume (0.0 to 1.0) - Note: tts_speaker.py will ignore this for now.
default_border_color: "#800080" # Fallback border color if camera not specified
camera_configurations:
# Define each camera that this notifier should handle.
# The 'topic_suffix' here corresponds to the MQTT topic your Node-RED
# will publish to for this camera's snapshots.
camera_one: # this would be the actual name of the camera found in mqtt (e.g. 'gardencam')
topic_suffix: "camera_one/snapshot" # an example might be 'gardencam/snapshot'
enabled_on_startup: true
border_color: "#FF4500" # OrangeRed
camera_two:
topic_suffix: "camera_two/snapshot"
enabled_on_startup: true
border_color: "#FFD700" # Gold
camera_three:
topic_suffix: "camera_three/snapshot"
enabled_on_startup: true
border_color: "#1E90FF" # DodgerBlue
camera_four:
topic_suffix: "camera_four/snapshot"
enabled_on_startup: true
border_color: "#32CD32" # LimeGreen
# Add new cameras here in the future, e.g.:
# camera_five:
# topic_suffix: "camera_five/snapshot"
# enabled_on_startup: true
# border_color: "#8A2BE2" # BlueViolet
tts_messages:
# Define specific TTS messages for each camera and detected object.
# These will be used by the notifier script.
camera_one:
person: "A person is in the back garden!"
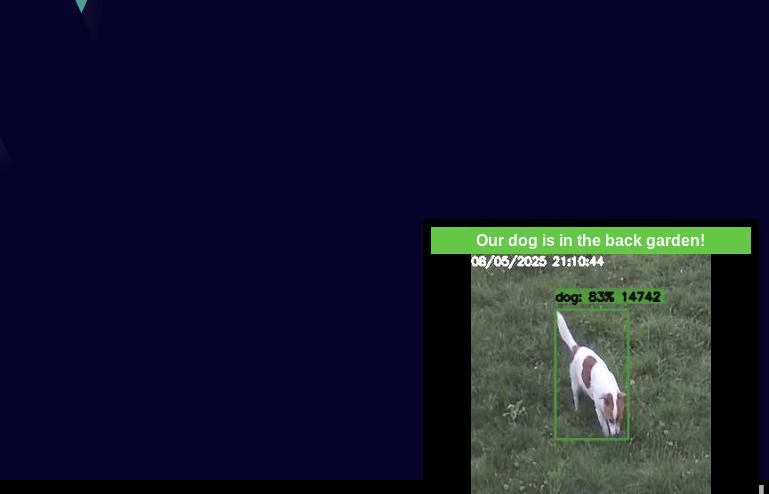
dog: "Our dog is in the back garden!"
camera_two:
person: "Person detected on the drive!"
car: "Car detected on the drive!"
camera_three:
person: "Person detected at the door!"
camera_four:
person: "Person detected to the right!"
car: "Car detected to the right!"
# Add default fallback message if no specific message is found
default: "Motion detected somewhere!"
mqtt: broker:: Change "YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_IP" to the actual IP address or hostname of your MQTT broker (e.g., 192.168.1.100).mqtt: password:: Change "YOUR_MQTT_PASSWORD" to the password you set for the MQTT user.camera_configurations::
camera_one, camera_two, etc.) to **exactly match your camera names in Frigate.**topic_suffix for each camera is unique and matches what you'll set up in Node-RED later (these are good defaults).border_color if you like!tts_messages:: This is where you make it personal! Change the messages for each camera and detected object. For example, if Frigate detects a person on your camera_one camera, it will use the camera_one: person: message. The default: message is used if no specific one is found.It's crucial to set up Python 3 within a virtual environment to manage dependencies properly and avoid conflicts with your system's Python installations.
Before proceeding, ensure you have Python 3 installed on your system. If not, follow the instructions below for your operating system.
sudo apt updatesudo apt install python3 python3-venvpython3 --versionYou should see an output like `Python 3.x.x`.
FrigateNotifier folder you created earlier (e.g., cd C:\Users\YOUR_WINDOWS_USERNAME\Documents\FrigateNotifier or cd ~/FrigateNotifier).python3 -m venv venv.\venv\Scripts\activatesource venv/bin/activateYou should see (venv) prefixing your command prompt, indicating the virtual environment is active.
With your virtual environment activated, install the required Python packages:
pip install gtts PyYAML Pillow paho-mqttNote for Windows users: You will also need to install `pywin32` for the Windows notifier script:
pip install pywin32Note for Debian/Linux users: You will also need to install `playsound` for the Debian notifier script:
pip install playsoundsudo apt install python3-gi python3-gst-1.0 gir1.2-gst-plugins-base-1.0sudo apt install libgstreamer1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-plugins-base gstreamer1.0-plugins-good gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-doc gstreamer1.0-tools gstreamer1.0-x gstreamer1.0-alsa gstreamer1.0-gl gstreamer1.0-gtk3 gstreamer1.0-qt5 gstreamer1.0-pulseaudiotts_speaker.py (Choose ONE based on your OS)This script handles all the text-to-speech magic. You will place one of the following two versions into your FrigateNotifier folder, and name it tts_speaker.py.
IMPORTANT: The tts_script_path in your config.yaml should be set to "tts_speaker.py". Ensure you only have *one* file named tts_speaker.py in your FrigateNotifier directory, and it should be the version appropriate for your operating system.
Important Note on Text-to-Speech (gTTS): The gTTS library relies on Google's online text-to-speech services. Therefore, your desktop computer running the notifier script must have an active internet connection for the voice alerts to work correctly."
This version uses `ffplay` (part of FFmpeg) for audio playback. You'll need to install FFmpeg separately.
Download and install FFmpeg from their official website: https://ffmpeg.org/download.html. Make sure to add the FFmpeg `bin` directory to your system's PATH environment variable so `ffplay` can be found by the script.
tts_speaker.py: In your FrigateNotifier folder, create a new file named tts_speaker.py.tts_speaker.py file.
# tts_speaker.py (ffplay version for Windows)
# This script takes a text string as a command-line argument and speaks it aloud using gTTS.
# It requires FFmpeg (specifically ffplay) to be installed and in your system's PATH.
import sys
import os
import logging
import tempfile
from gtts import gTTS
import subprocess
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - TTS_SPEAKER - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
def speak_text(text):
"""Generates speech using gTTS and plays it using ffplay."""
temp_audio_file = None
try:
logging.info(f"Attempting to speak: '{text}' using gTTS (en-uk voice)")
tts = gTTS(text=text, lang='en-uk', slow=False) # lang='en-uk' for British English
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=".mp3") as fp:
temp_audio_file = fp.name
tts.save(temp_audio_file)
logging.info(f"Speech saved to temporary file: {temp_audio_file}")
# Play the temporary audio file using ffplay (from FFmpeg)
# -nodisp: don't show a video window
# -autoexit: exit when playback finishes
# -i: input file
# creationflags=subprocess.CREATE_NO_WINDOW: IMPORTANT for silent operation on Windows
subprocess.run(['ffplay', '-nodisp', '-autoexit', '-i', temp_audio_file],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, check=True, timeout=10,
creationflags=subprocess.CREATE_NO_WINDOW)
logging.info("TTS playback complete.")
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error("ffplay command not found. Please ensure FFmpeg is installed and its 'bin' directory is in your system's PATH.")
logging.error("Download FFmpeg from https://ffmpeg.org/download.html")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
logging.error(f"ffplay failed with exit code {e.returncode}: {e.stderr.decode().strip()}")
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
logging.error("TTS script timed out after 10 seconds.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during gTTS generation or ffplay playback: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
finally:
if temp_audio_file and os.path.exists(temp_audio_file):
os.remove(temp_audio_file)
logging.info(f"Temporary audio file removed: {temp_audio_file}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
text_to_speak = sys.argv[1]
speak_text(text_to_speak)
else:
logging.warning("No text provided as a command-line argument. Usage: python tts_speaker.py 'Your text here'")
print("Usage: python tts_speaker.py 'Your text here'")
This version uses the `playsound` library for audio playback. It might require additional system dependencies on Linux.
tts_speaker.py: In your FrigateNotifier folder, create a new file named tts_speaker.py.tts_speaker.py file.
# tts_speaker.py (playsound version for Debian/Linux)
# This script takes a text string as a command-line argument and speaks it aloud using gTTS.
# It requires an internet connection to function.
import sys
import os
import logging
from gtts import gTTS
from playsound import playsound
import tempfile
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - TTS_SPEAKER - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
def speak_text(text):
"""Generates speech using gTTS and plays it."""
temp_audio_path = None
try:
logging.info(f"Attempting to speak: '{text}' using gTTS (en-uk voice)")
# Create gTTS object with British English voice in this example
# Using 'en' for language and 'co.uk' for top-level domain helps ensure British accent.
# Other choices American tld='com' Australian tld='com.au' Irish tld='ie' Indian English tld='co.in'
tts = gTTS(text=text, lang='en', tld='co.uk')
# Create a temporary file to save the speech audio
# Use a specific suffix to ensure it's recognized as an MP3
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=".mp3") as fp:
temp_audio_path = fp.name
tts.save(temp_audio_path)
logging.info(f"Speech saved to temporary file: {temp_audio_path}")
# Play the temporary audio file using playsound
playsound(temp_audio_path)
logging.info("TTS playback complete.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during gTTS or playsound: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
logging.error("This often indicates no internet connection, or missing audio playback dependencies (e.g., gstreamer on Linux for playsound).")
finally:
# Clean up the temporary audio file
if 'temp_audio_path' in locals() and os.path.exists(temp_audio_path):
try:
os.remove(temp_audio_path)
logging.info(f"Temporary audio file removed: {temp_audio_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.warning(f"Could not remove temporary audio file {temp_audio_path}: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
text_to_speak = sys.argv[1]
speak_text(text_to_speak)
else:
logging.warning("No text provided as a command-line argument. Usage: python tts_speaker.py 'Your text here'")
print("Usage: python tts_speaker.py 'Your text here'")
Node-RED acts as the brain that connects Frigate's raw messages to your desktop notifier. It processes events, grabs snapshots, and then sends a neatly packaged alert to your computer.
If you're already using Node-RED, you can skip this. Otherwise, the easiest way to run it alongside Home Assistant is via its official add-on.
config.yaml.This JSON block contains the entire Node-RED flow. This flow listens for Frigate events, finds the matching snapshot, combines them, encodes the image, and sends it all to your notifier's MQTT topic. It also includes the dashboard elements and volume control.
http://YOUR_HOME_ASSISTANT_IP:1880 or via the Home Assistant add-on web UI).If you haven't already, you'll need the Node-RED Dashboard nodes to display images and controls.
node-red-dashboard and click "Install".
IMPORTANT! Customise this flow for your cameras: The imported flow uses generic camera names (camera_one, camera_two, etc.). You must change these to the **exact names** you found for your own cameras earlier when you were finding your MQTT topics.
You will need to do the following for each of your cameras:
frigate/generic_name/person (or car, dog, etc.) with your camera's actual name (e.g., frigate/backgardencam/person). Do the same for the snapshot 'mqtt' in node (e.g., frigate/backgardencam/person/snapshot). Change the "Name" field to match.Join backgardencam person)function backgardencam person). Change all instances of the camera name and object to match your specific camera name and object name (e.g. frigate/backgardencam/person/snapshot) or (frigate/backgardencam/person)const msgForCameraOneDashboard = (cameraName === "camera_one") ? { payload: dashboardImagePayload } : null;. Change all instances of "camera_one", "camera_two", etc., to your specific camera names to ensure the dashboard images display correctly.h3tags to be descriptive for your cameras (e.g., Backgardencam).After importing, the nodes will appear on your canvas. You need to tell them which MQTT broker to use.
mqtt in or mqtt out nodes (e.g., "Frigate Camera Four Person Event").Your MQTT Broker (or any name you prefer)YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100) - **This must match the IP in your config.yaml!**1883mqtt_ntfy (or your MQTT username)YOUR_MQTT_PASSWORD (or your MQTT password) - **This must match the password in your config.yaml!**Quick Explanation of the Flow (Updated for Join Node):
Remember to configure the MQTT Broker in Node-RED for EACH MQTT node. Double-click the MQTT nodes and ensure they point to your actual MQTT broker using the pencil icon. The example flow uses `your_mqtt_broker_config_id` as a placeholder.
http://YOUR_HOME_ASSISTANT_IP:1880/ui. You should see the live image display and the control switches.This is the Python script that runs on your desktop, constantly listening for MQTT messages from Node-RED. When it receives a message, it pops up the image and plays the TTS message.
win_notifier.py)This script is tailored for Windows, using tkinter for the pop-up window and `win32api`/`win32gui` for fullscreen detection.
win_notifier.py: In your FrigateNotifier folder (the same one with config.yaml and tts_speaker.py), create a new file named win_notifier.py. Again, remember to change "Save as type" to "All Files (*.)" and add the `.py` extension manually if using Notepad.win_notifier.py file.
# --- SCRIPT VERSION: 20250717.08 (JSON Payload & Config TTS - Compatible with User's gTTS) ---
# This version expects JSON payload with image_data and detected_label from Node-RED.
# It calls tts_speaker.py without a volume argument to match the user's provided script.
# --- IMMEDIATE DEBUGGING START ---
import sys
import subprocess # For calling external TTS script
import threading # For TTS queue, image queue, and fullscreen monitor
import collections # For deque (double-ended queue)
import os # For path manipulation
sys.stdout.reconfigure(line_buffering=True)
sys.stderr.reconfigure(line_buffering=True)
print("DEBUG: Script started. Attempting imports...")
# --- IMMEDIATE DEBUGGING END ---
import logging
import time
import json
import tkinter as tk
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
# Use a try-except block for critical imports to catch issues early
try:
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
import win32api
import win32gui
import yaml # New import for YAML parsing
print("DEBUG: All core imports successful.")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"CRITICAL ERROR: Failed to import a required module: {e}")
print("Please ensure all Python libraries are installed. Run: pip install paho-mqtt Pillow pywin32 PyYAML") # Added PyYAML
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"CRITICAL ERROR: An unexpected error occurred during imports: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler()])
# --- Configuration File Path ---
CONFIG_FILE = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), "config.yaml")
# Function to load configuration from YAML file
def load_config():
try:
with open(CONFIG_FILE, 'r') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f)
logging.info(f"Configuration loaded from {CONFIG_FILE}")
return config
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error(f"ERROR: Configuration file not found at {CONFIG_FILE}. Please create it.")
sys.exit(1)
except yaml.YAMLError as e:
logging.error(f"ERROR: Error parsing configuration file {CONFIG_FILE}: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"ERROR: An unexpected error occurred while loading config: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
# Load configuration at script start
app_config = load_config()
# --- MQTT Configuration (Loaded from config.yaml) ---
MQTT_BROKER = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('broker', '127.0.0.1')
MQTT_PORT = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('port', 1883)
MQTT_USERNAME = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('username', None)
MQTT_PASSWORD = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('password', None)
# Base MQTT topic for receiving camera snapshots (must match Node-RED)
MQTT_SNAPSHOT_BASE_TOPIC = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('snapshot_base_topic', 'notifier/')
# MQTT topic for receiving control commands (e.g., from Node-RED dashboard)
MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC = app_config.get('mqtt', {}).get('control_topic', 'notifier/control')
IMAGE_CACHE_DIR = os.path.join(os.environ.get('LOCALAPPDATA', os.path.expanduser('~')), app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('image_cache_dir', 'MotionNotifierCache'))
# Initial check for the directory - this should run once on script start
try:
os.makedirs(IMAGE_CACHE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
logging.info(f"Image cache directory: {IMAGE_CACHE_DIR}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"CRITICAL ERROR: Could not create image cache directory '{IMAGE_CACHE_DIR}': {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
# --- Notification Specifics (General) ---
COOLDOWN_PERIOD = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('cooldown_period_seconds', 10) # seconds
# --- Large Image Pop-up Settings (using Tkinter for a single, queued pop-up) ---
ENABLE_LARGE_IMAGE_POPUP = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('enable_large_image_popup', True)
LARGE_IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('large_image_display_duration_seconds', 5) # seconds
# Fixed dimensions for the single pop-up window
IMAGE_DISPLAY_WIDTH = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('image_display_width', 320)
IMAGE_DISPLAY_HEIGHT = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('image_display_height', 240)
# Fixed position for the single pop-up window (bottom-right)
FIXED_OFFSET_X = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('fixed_offset_x', 10)
FIXED_OFFSET_Y = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('fixed_offset_y', 10)
# --- Custom Border and Text Settings ---
BORDER_WIDTH = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('border_width', 3)
WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('window_internal_padding', 5)
TEXT_LABEL_HEIGHT_ESTIMATE = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('text_label_height_estimate', 25)
# Define border colors for each camera (now loaded from config)
# Default to a fallback if not found in config
CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS = {
cam_name: cam_cfg.get('border_color', '#800080') # Default to Purple if not specified
for cam_name, cam_cfg in app_config.get('camera_configurations', {}).items()
}
# Add a default fallback for any camera not explicitly listed in config
CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS['default'] = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('default_border_color', '#800080')
# --- Text-to-Speech (TTS) Settings ---
ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('tts_enabled_on_startup', True)
TTS_SCRIPT_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('tts_script_path', 'tts_speaker.py'))
# TTS_PREFIX is now less critical as specific messages are loaded, but kept for fallback consistency
TTS_PREFIX = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('tts_prefix', 'Motion detected at the ')
# Initial TTS volume loaded from config.yaml (this will be passed, but tts_speaker.py will ignore it for now)
initial_tts_volume_config = app_config.get('general_settings', {}).get('initial_volume', 1.0)
# Global variable for TTS volume, controlled by MQTT. Initialized from config.
current_tts_volume = max(0.0, min(1.0, float(initial_tts_volume_config)))
logging.info(f"Initial TTS volume set to {current_tts_volume} (from config.yaml).")
# Load specific TTS messages from config.yaml
TTS_MESSAGES = app_config.get('tts_messages', {})
logging.info(f"Loaded TTS messages from config: {TTS_MESSAGES}")
# Lock and Queue for TTS to ensure sequential announcements
tts_lock = threading.Lock()
tts_queue = collections.deque()
# --- Camera-specific configurations (now loaded from config.yaml) ---
CAMERA_CONFIGS = app_config.get('camera_configurations', {})
# Initialize cooldown timers for cameras if they weren't loaded from config
for cam_name, cam_cfg in CAMERA_CONFIGS.items():
if "cooldown_timer" not in cam_cfg:
cam_cfg["cooldown_timer"] = 0
# Ensure 'enabled' state is set from config, defaulting to True
if "enabled_on_startup" not in cam_cfg:
cam_cfg["enabled"] = True
else:
cam_cfg["enabled"] = cam_cfg["enabled_on_startup"]
# --- Global State for Fullscreen Detection ---
IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE = False
last_fullscreen_state = False # To log state changes only
# --- Tkinter Root Window (initialized once in main thread) ---
root = None
# Image display queue and lock
image_display_queue = collections.deque()
image_queue_lock = threading.Lock()
current_popup_window = None # Reference to the currently displayed Tkinter window
# --- Image Popup Class (uses Tkinter) ---
class ImagePopup:
def __init__(self, master, camera_name, image_path, display_duration, final_width, final_height, x_pos, y_pos, border_color, label_text):
logging.info(f"ImagePopup: Initializing for {camera_name} at fixed position {x_pos},{y_pos} with total size {final_width}x{final_height}")
self.master = master
self.camera_name = camera_name
self.image_path = image_path
self.display_duration = display_duration
self.total_window_width = final_width
self.total_window_height = final_height
self.window = tk.Toplevel(master)
self.window.attributes('-topmost', True)
self.window.overrideredirect(True) # Remove window decorations (title bar, border)
self.window.config(bg='black') # Set window background to black
self.window.withdraw() # Hide it immediately after creation
self.border_frame = tk.Frame(self.window, bg=border_color, bd=BORDER_WIDTH, relief='solid')
self.border_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING, pady=WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING)
self.text_label = tk.Label(self.border_frame, text=label_text, fg='white', bg=border_color, font=('Arial', 12, 'bold'))
self.text_label.pack(side=tk.TOP, pady=2)
self.image_label = tk.Label(self.border_frame, bg='black') # Set label background to black
self.image_label.pack(side=tk.TOP, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True) # Image label fills remaining space
self.load_image_for_display() # This will now determine the actual image size within the label
# Set window geometry using actual image dimensions and calculated position
self.window.geometry(f"{self.total_window_width}x{self.total_window_height}+{x_pos}+{y_pos}") # Use fixed total window size
logging.info(f"ImagePopup: Window geometry set to {self.total_window_width}x{self.total_window_height}+{x_pos}+{y_pos}")
self.window.update_idletasks() # Ensure all pending geometry calculations are done
# Only deiconify if not in fullscreen mode
if not IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE:
self.window.deiconify()
logging.info(f"Image popup for {camera_name} deiconified (shown).")
else:
logging.info(f"Image popup for {camera_name} kept hidden due to fullscreen mode.")
def load_image_for_display(self):
try:
pil_image = Image.open(self.image_path)
logging.debug(f"DEBUG: Original image size for {self.camera_name}: {pil_image.width}x{pil_image.height}")
# Calculate image size based on total window size minus border, padding, and text area
image_target_width = self.total_window_width - (2 * BORDER_WIDTH) - (2 * WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING)
image_target_height = self.total_window_height - TEXT_LABEL_HEIGHT_ESTIMATE - (2 * BORDER_WIDTH) - (2 * WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING) - 2 # -2 for minor adjustments
pil_image.thumbnail((image_target_width, image_target_height), Image.LANCZOS)
logging.debug(f"DEBUG: Thumbnail image size for {self.camera_name}: {pil_image.width}x{pil_image.height}")
if pil_image.width == 0 or pil_image.height == 0:
logging.error(f"Error: Resized image for {self.camera_name} has zero dimensions. Skipping.")
# Set a minimal size to avoid Tkinter errors, though image won't be visible
self.actual_image_width = 1
self.actual_image_height = 1
return
self.tk_image = ImageTk.PhotoImage(pil_image)
self.image_label.config(image=self.tk_image)
self.image_label.image = self.tk_image # Keep a reference!
# Store actual dimensions of the resized image (within the label)
self.actual_image_width = pil_image.width
self.actual_image_height = pil_image.height
logging.info(f"Image loaded into label for {self.camera_name}: {self.image_path} (Actual size: {self.actual_image_width}x{self.actual_image_height})")
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error(f"Image file not found for popup: {self.image_path}")
# Do not destroy window here, let the queue processor handle it
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error loading image into popup: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
# Do not destroy window here, let the queue processor handle it
def destroy_window(self):
if self.window.winfo_exists():
self.window.destroy()
logging.info(f"Image popup for {self.camera_name} destroyed.")
# --- Function to check for fullscreen status ---
def check_fullscreen_status():
global IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE, last_fullscreen_state, current_popup_window
screen_width = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(0)
screen_height = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(1)
try:
hwnd = win32gui.GetForegroundWindow()
rect = win32gui.GetWindowRect(hwnd)
current_fullscreen_state = (rect[0] == 0 and rect[1] == 0 and rect[2] == screen_width and rect[3] == screen_height)
if current_fullscreen_state and not last_fullscreen_state:
logging.info("Fullscreen application detected. Image pop-ups will be suppressed.")
if current_popup_window and current_popup_window.window.winfo_exists():
current_popup_window.window.withdraw() # Hide the current popup
logging.info(f"Hidden current popup ({current_popup_window.camera_name}) due to fullscreen.")
elif not current_fullscreen_state and last_fullscreen_state:
logging.info("Fullscreen application no longer detected. Image pop-ups re-enabled.")
if current_popup_window and current_popup_window.window.winfo_exists() and not current_popup_window.window.winfo_ismapped():
current_popup_window.window.deiconify() # Show the current popup if it was hidden
logging.info(f"Reshown current popup ({current_popup_window.camera_name}) as fullscreen exited.")
IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE = current_fullscreen_state
last_fullscreen_state = current_fullscreen_state
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error checking fullscreen status: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
# --- Thread for periodic fullscreen check ---
def fullscreen_monitor_thread():
while True:
check_fullscreen_status()
time.sleep(5)
# --- Queue Processor Threads ---
def display_queue_processor():
global root, current_popup_window, IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE
while True:
try:
# Wait for an item in the queue
with image_queue_lock:
if not image_display_queue:
# If queue is empty, release lock and wait a bit before checking again
time.sleep(0.1)
continue
# Get the next item from the queue
camera_name, temp_image_path, config, label_text = image_display_queue.popleft() # Added label_text
logging.info(f"Processing image from queue for {camera_name}. Image Queue size: {len(image_display_queue)}")
# Calculate total window dimensions based on fixed image size plus border, padding, and text area
total_window_width = IMAGE_DISPLAY_WIDTH + (2 * BORDER_WIDTH) + (2 * WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING)
total_window_height = IMAGE_DISPLAY_HEIGHT + TEXT_LABEL_HEIGHT_ESTIMATE + (2 * BORDER_WIDTH) + (2 * WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING) + 2
screen_width = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screen_height = root.winfo_screenheight()
# Fixed position: bottom-right
x_pos = screen_width - total_window_width - FIXED_OFFSET_X
y_pos = screen_height - total_window_height - FIXED_OFFSET_Y
logging.info(f"DEBUG: Calculated popup position for {camera_name}: x_pos={x_pos}, y_pos={y_pos}")
# Destroy any currently active popup before creating a new one
if current_popup_window and current_popup_window.window.winfo_exists():
logging.info(f"Destroying current popup for {current_popup_window.camera_name} to show next image.")
current_popup_window.destroy_window()
current_popup_window = None
logging.info(f"DEBUG: Attempting to create new ImagePopup for {camera_name} on main thread.")
# Create the new ImagePopup on the main Tkinter thread
# Use root.after to safely interact with Tkinter from another thread
event = threading.Event() # To wait for popup creation to complete
root.after(0, lambda: _create_image_popup_on_main_thread_synced(
camera_name, temp_image_path, total_window_width, total_window_height,
x_pos, y_pos, CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS.get(camera_name, CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS["default"]),
label_text, event # Pass label_text here
))
event.wait() # Wait for the popup to be created on the main thread
logging.info(f"DEBUG: ImagePopup creation for {camera_name} signalled complete.")
# Keep the image displayed for the duration
logging.info(f"DEBUG: Displaying image for {LARGE_IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION} seconds.")
time.sleep(LARGE_IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION)
# Destroy the popup after its display duration
if current_popup_window and current_popup_window.window.winfo_exists():
logging.info(f"DEBUG: Destroying image popup for {current_popup_window.camera_name} after display duration.")
current_popup_window.destroy_window()
current_popup_window = None
# Clean up the temporary image file
if os.path.exists(temp_image_path):
os.remove(temp_image_path)
logging.info(f"Cleaned up temporary audio file removed: {temp_image_path}") # Corrected log message
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in display_queue_processor: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
# Ensure the current_popup_window is cleared on error to prevent blocking
if current_popup_window and current_popup_window.window.winfo_exists():
current_popup_window.destroy_window()
current_popup_window = None
time.sleep(1) # Prevent busy-looping on persistent errors
# Helper function to create ImagePopup on main Tkinter thread
def _create_image_popup_on_main_thread_synced(camera_name, temp_image_path, total_window_width, total_window_height, x_pos, y_pos, border_color, label_text, event):
global root, current_popup_window
try:
current_popup_window = ImagePopup(root, camera_name, temp_image_path, LARGE_IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION,
total_window_width, total_window_height, x_pos, y_pos, border_color, label_text)
logging.info(f"ImagePopup instance created on main thread for {camera_name}.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error creating ImagePopup on main thread: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
finally:
event.set() # Signal that creation attempt is complete
def tts_processor():
"""Processes TTS messages from the queue sequentially."""
global ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION
while True:
try:
with tts_lock: # Acquire lock to ensure only one TTS plays at a time
if not tts_queue:
time.sleep(0.1) # Small sleep if queue is empty
continue
# Get message, script path, python executable. Volume is NOT passed to tts_speaker.py
message_to_speak, tts_script_path, venv_python_executable = tts_queue.popleft()
logging.info(f"Processing TTS from queue: '{message_to_speak}'. TTS Queue size: {len(tts_queue)}")
if ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION:
try:
# Pass only the message to tts_speaker.py, matching the user's provided script
subprocess.run([venv_python_executable, tts_script_path, message_to_speak],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, check=True, timeout=10)
logging.info(f"Launched TTS for: '{message_to_speak}' (completed).")
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error(f"TTS script or Python interpreter not found. Ensure '{venv_python_executable}' and '{tts_script_path}' exist.")
logging.error("If ffplay error, ensure FFmpeg is installed and its 'bin' directory is in your system's PATH.")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
logging.error(f"TTS script failed with exit code {e.returncode}: {e.stderr.decode().strip()}")
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
logging.error("TTS script timed out after 10 seconds.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error launching TTS script: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
else:
logging.info(f"TTS notification disabled. Skipping: '{message_to_speak}'")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in TTS processor: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
time.sleep(0.01) # Small delay to prevent busy-looping on persistent errors
# --- MQTT Callbacks ---
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc, properties):
if rc == 0:
logging.info(f"Connected to MQTT Broker: {userdata['broker_address']}:{userdata['broker_port']}")
for camera_name, config in userdata['CAMERA_CONFIGS'].items(): # Access CAMERA_CONFIGS from userdata
full_topic = userdata['MQTT_SNAPSHOT_BASE_TOPIC'] + config["topic_suffix"]
client.subscribe(full_topic)
logging.info(f"Subscribed to snapshot topic: {full_topic}")
client.subscribe(userdata['MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC']) # Access MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC from userdata
logging.info(f"Subscribed to control topic: {userdata['MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC']}")
else:
logging.error(f"Failed to connect to MQTT, return code {rc}")
logging.error("Retrying connection in run_notifier loop...")
def on_message(client, userdata, msg):
# --- IMPORTANT: Declare global variables used in this function ---
# Only IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE, ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION, and current_tts_volume need to be global
# as they are modified by other threads/control messages.
global IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE, ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION, current_tts_volume
current_time = time.time()
# --- Handle Control Messages ---
if msg.topic == userdata['MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC']:
try:
control_payload = json.loads(msg.payload.decode('utf-8'))
logging.info(f"Received control message: {control_payload}")
camera_name = control_payload.get("camera_name") # Can be 'all' or specific camera name
action = control_payload.get("action")
value = control_payload.get("value")
if action == "set_enabled" and isinstance(value, bool):
if camera_name == "all":
for cam_cfg in CAMERA_CONFIGS.values():
cam_cfg["enabled"] = value
logging.info(f"All cameras set to enabled={value}")
elif camera_name in CAMERA_CONFIGS:
CAMERA_CONFIGS[camera_name]["enabled"] = value
logging.info(f"Camera '{camera_name}' set to enabled={value}")
else:
logging.warning(f"Control message for unknown camera: '{camera_name}'.")
elif action == "set_tts_enabled" and isinstance(value, bool):
ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION = value
logging.info(f"TTS notifications set to enabled={ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION}")
elif action == "set_volume" and isinstance(value, (int, float)): # Handle volume control
current_tts_volume = max(0.0, min(1.0, float(value))) # Ensure volume is 0.0-1.0
logging.info(f"TTS volume set to {current_tts_volume} (from control message).")
# --- NEW CODE START ---
elif action == "speak_message" and isinstance(value, str):
if ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION:
logging.info(f"Received 'speak_message' action. Adding '{value}' to TTS queue.")
# Pass the received message directly to the TTS queue
tts_queue.append((value, userdata['TTS_SCRIPT_PATH'], userdata['VENV_PYTHON_EXECUTABLE']))
else:
logging.info(f"TTS notifications are disabled. Skipping custom message: '{value}'")
# --- NEW CODE END ---
else:
logging.warning(f"Unknown action '{action}' or invalid value for control message.")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
logging.error(f"Failed to decode control message JSON: {msg.payload.decode('utf-8')}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error processing control message: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
return
# --- Handle Snapshot Messages ---
for camera_name, config in userdata['CAMERA_CONFIGS'].items(): # Access CAMERA_CONFIGS from userdata
full_topic = userdata['MQTT_SNAPSHOT_BASE_TOPIC'] + config["topic_suffix"]
if msg.topic == full_topic:
# Parse the incoming MQTT payload as a UTF-8 JSON string
payload_data = {} # Initialize to empty dict
image_data_base64 = None
detected_label = "unknown" # Default label
try:
# Node-RED is now expected to send a JSON string
payload_string = msg.payload.decode('utf-8')
payload_data = json.loads(payload_string)
image_data_base64 = payload_data.get('image_data')
detected_label = payload_data.get('detected_label', 'unknown')
logging.info(f"Parsed JSON payload for {camera_name}. Detected Label: {detected_label}")
except (UnicodeDecodeError, json.JSONDecodeError) as e:
# If decoding or JSON parsing fails, it means Node-RED didn't send JSON as expected.
# Log the error and fall back to 'unknown' label and no image display.
logging.error(f"Failed to decode/parse MQTT payload as JSON for {camera_name}: {type(e).__name__}: {e}. Payload: '{msg.payload.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')}'")
logging.warning("Expected JSON payload from Node-RED, but received invalid data. Skipping image display and using default TTS.")
image_data_base64 = None # Ensure no image is processed if payload is bad
detected_label = "unknown" # Fallback label
# On Linux, we're not suppressing pop-ups for fullscreen initially
# if IS_FULLSCREEN_ACTIVE:
# logging.info(f"Skipping image pop-up for '{camera_name}': Fullscreen application detected.")
# # We still want TTS if enabled, even if image is skipped
# if ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION:
# message_to_speak = TTS_MESSAGES.get(camera_name, {}).get(detected_label, TTS_MESSAGES.get('default', "Motion detected!"))
# tts_queue.append((message_to_speak, userdata['TTS_SCRIPT_PATH'], userdata['VENV_PYTHON_EXECUTABLE']))
# logging.info(f"Added TTS for: '{message_to_speak}' to queue due to fullscreen.")
# return
if not config["enabled"]:
logging.info(f"Camera '{camera_name}' is disabled. Skipping notification.")
return
if current_time - config["cooldown_timer"] < userdata['COOLDOWN_PERIOD']: # Access COOLDOWN_PERIOD from userdata
logging.info(f"Notification for '{camera_name}' on cooldown. Skipping. Time remaining: {userdata['COOLDOWN_PERIOD'] - (current_time - config['cooldown_timer']):.1f}s")
return
userdata['CAMERA_CONFIGS'][camera_name]["cooldown_timer"] = current_time
logging.info(f"Received snapshot from topic '{msg.topic}' (Camera: {camera_name}, Label: {detected_label})")
# --- Determine TTS Message from config.yaml ---
# Use .get() with a default for camera and label to prevent KeyError
message_to_speak = TTS_MESSAGES.get(camera_name, {}).get(detected_label, TTS_MESSAGES.get('default', "Motion detected!"))
logging.info(f"Determined TTS message from config: '{message_to_speak}'")
# --- TTS Notification (add to TTS queue) ---
if ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION: # Use the global state
# Add message, script path, python executable to the TTS queue
tts_queue.append((message_to_speak, userdata['TTS_SCRIPT_PATH'], userdata['VENV_PYTHON_EXECUTABLE']))
logging.info(f"Added TTS for: '{message_to_speak}' to queue. TTS Queue size: {len(tts_queue)}")
temp_image_path = None
if image_data_base64: # Only proceed if base64 image data was successfully extracted
try:
import base64
raw_image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data_base64)
timestamp = int(time.time() * 1000)
image_filename = f"{camera_name}_{detected_label}_snapshot_{timestamp}.jpg" # Include label in filename
temp_image_path = os.path.join(userdata['image_cache_dir'], image_filename)
logging.info(f"Saving image to {temp_image_path}")
with open(temp_image_path, 'wb') as handler:
handler.write(raw_image_bytes)
logging.info(f"Image saved successfully to {temp_image_path}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding or saving image for '{camera_name}': {type(e).__name__}: {e}")
temp_image_path = None
else:
logging.warning(f"No valid image data found in payload for {camera_name}. Skipping image display.")
if userdata['ENABLE_LARGE_IMAGE_POPUP'] and temp_image_path:
# Add image display request to the queue, passing the determined TTS message as label_text
image_display_queue.append((camera_name, temp_image_path, config, message_to_speak))
logging.info(f"Added image for {camera_name} to display queue. Image Queue size: {len(image_display_queue)}")
break
else:
logging.warning(f"Received message on unexpected topic: {msg.topic}")
# --- Main execution ---
def run_notifier():
global root
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
root.title("Motion Notifier Background (Debian)") # Changed title for Linux
# Determine the path to the virtual environment's python.exe (or python on Linux)
# This assumes motion_notifier.py is run from the venv, so sys.executable points to venv's python
venv_python_executable = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sys.executable), "python") # Changed to 'python' for Linux
logging.info(f"DEBUG: Determined VENV_PYTHON_EXECUTABLE: {venv_python_executable}")
# Populate client_userdata with all necessary configurations
client_userdata = {
'broker_address': MQTT_BROKER,
'broker_port': MQTT_PORT,
'image_cache_dir': IMAGE_CACHE_DIR,
'CAMERA_CONFIGS': CAMERA_CONFIGS, # Pass the entire CAMERA_CONFIGS dictionary
'COOLDOWN_PERIOD': COOLDOWN_PERIOD,
'ENABLE_LARGE_IMAGE_POPUP': ENABLE_LARGE_IMAGE_POPUP,
'IMAGE_DISPLAY_WIDTH': IMAGE_DISPLAY_WIDTH,
'IMAGE_DISPLAY_HEIGHT': IMAGE_DISPLAY_HEIGHT,
'IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION': LARGE_IMAGE_DISPLAY_DURATION,
'FIXED_OFFSET_X': FIXED_OFFSET_X,
'FIXED_OFFSET_Y': FIXED_OFFSET_Y,
'MQTT_SNAPSHOT_BASE_TOPIC': MQTT_SNAPSHOT_BASE_TOPIC,
'MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC': MQTT_CONTROL_TOPIC,
'ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION': ENABLE_TTS_NOTIFICATION,
'TTS_SCRIPT_PATH': TTS_SCRIPT_PATH,
#'TTS_PREFIX': TTS_PREFIX,
'VENV_PYTHON_EXECUTABLE': venv_python_executable,
'CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS': CAMERA_BORDER_COLORS,
'BORDER_WIDTH': BORDER_WIDTH,
'WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING': WINDOW_INTERNAL_PADDING,
'TEXT_LABEL_HEIGHT_ESTIMATE': TEXT_LABEL_HEIGHT_ESTIMATE,
}
client = mqtt.Client(mqtt.CallbackAPIVersion.VERSION2)
client.user_data_set(client_userdata)
client.on_connect = on_connect
client.on_message = on_message
if MQTT_USERNAME and MQTT_PASSWORD:
client.username_pw_set(MQTT_USERNAME, MQTT_PASSWORD)
logging.info("MQTT client configured with username/password.")
else:
logging.warning("WARNING: MQTT client connecting without username/password. Ensure your broker allows anonymous access or provide credentials.")
while True:
try:
logging.info(f"Attempting to connect to MQTT broker at {MQTT_BROKER}:{MQTT_PORT}...")
client.connect(MQTT_BROKER, MQTT_PORT, 60)
logging.info("MQTT connection attempt successful.")
break
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Could not connect to MQTT broker: {type(e).__name__}: {e}. Retrying in 5 seconds...")
time.sleep(5)
client.loop_start()
logging.info("MQTT client loop started in background thread.")
# Fullscreen monitor thread is removed for Linux simplicity
# fullscreen_thread = threading.Thread(target=fullscreen_monitor_thread)
# fullscreen_thread.daemon = True
# fullscreen_thread.start()
# logging.info("Fullscreen monitor thread started.")
# Start the TTS queue processor in a separate daemon thread
tts_processor_thread = threading.Thread(target=tts_processor)
tts_processor_thread.daemon = True
tts_processor_thread.start()
logging.info("TTS queue processor thread started.")
# Start the image display queue processor in a separate daemon thread
image_queue_processor_thread = threading.Thread(target=display_queue_processor)
image_queue_processor_thread.daemon = True
image_queue_processor_thread.start()
logging.info("Image display queue processor thread started.")
logging.info("Starting Tkinter mainloop for GUI management.")
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_notifier()
```pip install Pillowtkinter (if missing): On some Debian/Ubuntu systems, tkinter might not be installed by default. You can install it with:
sudo apt install python3-tkOpen your terminal, navigate to the FrigateNotifier folder, activate your virtual environment, and run:
source venv/bin/activatepython deb_notifier.pyKeep this terminal window open. It will show log messages and spawn the pop-ups.
For Debian-based systems (like Ubuntu), `systemd` is the standard way to manage services that run automatically on startup. This will allow your notifier to start in the background when your desktop environment loads.
Open a terminal and create a new systemd service file for your user. This ensures it runs after your graphical session starts.
nano ~/.config/systemd/user/frigate-notifier.serviceIf the `user` directory doesn't exist, you might need to create it first: `mkdir -p ~/.config/systemd/user`
Paste the following content into the `frigate-notifier.service` file:
[Unit]
Description=Frigate Desktop Notifier
After=graphical-session.target network-online.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/home/YOUR_USERNAME/FrigateNotifier/venv/bin/python /home/YOUR_USERNAME/FrigateNotifier/deb_notifier.py
WorkingDirectory=/home/YOUR_USERNAME/FrigateNotifier
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=graphical-session.target
YOUR_USERNAME with your actual Debian/Linux username in both the `ExecStart` and `WorkingDirectory` lines.In the terminal, run these commands to reload systemd and enable your new service:
systemctl --user daemon-reload
systemctl --user enable frigate-notifier.service
systemctl --user start frigate-notifier.serviceThe `systemctl --user start frigate-notifier.service` command will start the notifier immediately. It will then automatically start on future logins.
To check if the service is running correctly, use:
systemctl --user status frigate-notifier.serviceWhile this guide focuses on Windows and Debian, the core Python notifier script (deb_notifier.py, or `win_notifier.py` if adapted) is largely cross-platform, especially the MQTT communication and image/TTS queuing logic. However, certain aspects will require adjustments for other operating systems:
The Python 3 and virtual environment setup (Section 1.C) is generally applicable. You'll still need to install gtts, PyYAML, Pillow, and paho-mqtt via `pip` within your virtual environment.
tts_speaker.py):
The `tts_speaker.py` script uses either `ffplay` (Windows) or `playsound` (Debian). For other operating systems:
Tkinter is a standard Python GUI library and should work across most desktop environments where Python is installed. If you encounter issues, ensure your system has the Tkinter development packages installed (e.g., `python3-tk` on Debian/Ubuntu, `python3-tkinter` on Fedora, or similar for macOS). The pop-up positioning logic might need minor adjustments depending on how different desktop environments handle window geometry.
The `win_notifier.py` script includes Windows-specific `win32api`/`win32gui` calls for fullscreen detection. This functionality is generally OS-specific and would need to be re-implemented using native APIs for macOS or other Linux desktop environments (e.g., X11/Wayland APIs for Linux). For simplicity, the `deb_notifier.py` version omits fullscreen detection, which might be a reasonable approach for other OSes if a robust cross-platform solution isn't easily found.
This is the most OS-dependent part. You'll need to research the standard method for running user-specific applications on startup for your chosen operating system:
By understanding these general principles, you should be able to adapt the provided scripts to a wider range of desktop operating systems.
Now that your desktop notifier is ready to receive messages and snapshots, we can set up the Home Assistant side. This involves creating a helper, a script, and an automation to send custom text messages to your desktop for speech output.
input_boolean.desktop_notifier_tts_enabledThis helper acts as a master on/off switch for your desktop TTS notifications. You can toggle it from your dashboard or use another automation to control it.
To create this helper, go to Settings > Devices & Services > Helpers and click "Create Helper". Choose "Toggle" and give it the name Desktop Notifier TTS Enabled.
Alternatively, you can add it to your configuration.yaml or a dedicated helpers.yaml file:
input_boolean:
desktop_notifier_tts_enabled:
name: Desktop Notifier TTS Enabled
initial: on
icon: mdi:volume-high
script.desktop_notifier_speakThis script is the central tool for sending text messages to your notifier via MQTT. It accepts a message field and publishes it to the notifier/control topic.
You can create this script by going to Settings > Automations & Scenes > Scripts and creating a new script. Paste this YAML into the script editor.
alias: desktop_notifier_speak
description: Sends a custom text message to the desktop notifier for speech output.
fields:
message:
name: Message
description: The text message to be spoken by the desktop notifier.
required: true
selector:
text: null
sequence:
- data:
topic: notifier/control
payload: |
{"action": "speak_message", "value": "{{ message }}"}
qos: "0"
retain: false
action: mqtt.publish
mode: single
This automation ties everything together. It listens for a trigger event, checks the input_boolean helper as a condition, and then calls the desktop_notifier_speak script with your custom message.
alias: Front Door Opened - Speak Notification
description: Speaks a message on the desktop when the front door opens, if TTS is enabled.
trigger:
- platform: state
entity_id: binary_sensor.front_door_contact # Replace with your door sensor's entity_id
to: "on"
condition:
- condition: state
entity_id: input_boolean.desktop_notifier_tts_enabled
state: "on"
action:
- service: script.desktop_notifier_speak
data:
message: "The front door has just been opened."
mode: single
Please note: There is one quirk I can't iron out, after restarting the machine or the scrip it with run through all the cameras once, notifying each.
Congratulations! You now have a powerful, custom desktop notification system for your Frigate and Home Assistant events.